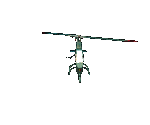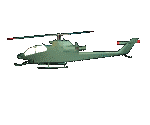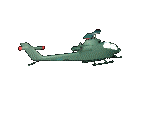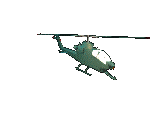鐵之狂傲
標題: 『每日軍武』- AH-1W超級眼鏡蛇(Super Cobra)攻擊直昇機 [列印本頁]
作者: 克里斯Chris 時間: 06-12-30 09:49
標題: 『每日軍武』- AH-1W超級眼鏡蛇(Super Cobra)攻擊直昇機
AH-1W Super Cobra
AH-1W超級眼鏡蛇攻擊直昇機

原文:
In 1966, the DOD contracted with Bell Helicopter, Inc. (BHI) for 1,100 AH-1G aircraft, which logged more than 1 million flight hours in Vietnam. Subsequently, the USMC desired a twin engine AH-1G; thus, the SEA COBRA (AH-1J) was developed. The United States Marine Corps (USMC) then identified a need for more armaments; thus, the AH-1T upgrade was initiated. This aircraft had an extended tailboom and fuselage and an upgraded transmission and engines.
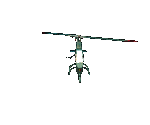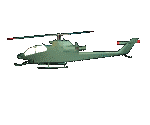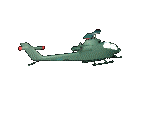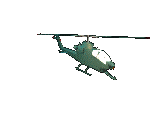
The AH-1 is fully capable of performing its attack mission in all weather conditions. Additional missions include direct air support, antitank, armed escort, and air to air combat.
The TOW missile targeting system uses a telescopic sight unit (traverse 110? elevation 60?+30?, a laser augmented tracking capability, thermal sights and a FLIR to allow for acquisition, launch, and tracking of all types of TOW missiles in all weather conditions. The Cobra also uses a digital ballistic computer, a HUD, Doppler nav, and a low speed air data sensor on the starboard side for firing, and has in-flight boresighting. External stores are mounted on underwing external stores points.
Each wing has two hardpoints for a total of four stations. A representative mix when targeting armor formations would be eight TOW missiles, two 2.75-in rocket pods, and 750x 20-mm rounds. The gun must be centered before firing underwing stores. Armored cockpit can withstand small arms fire, and composite blades and tailboom are able withstand damage from 23-mm cannon hits.small arms fire, and composite blades and tailboom able to withstand damage from 23-mm cannon hits.
The Marines depend on attack helicopters to provide close-in fire support coordination in serial and ground escort operations. Such support is required during amphibious ship-to-shore movements and subsequent shore operations within the objective area. AH-1 is designed for the following tasks:
Armed escort for helicopters carrying personnel and cargoLanding zone fire suppression supportVisual armed reconnaissanceTarget marking and direction for high-performance attack aircraftConvoy escort and fire suppression for ground unitsOperations from air capable shipsPoint target attack of threatening armorSelf-defense and protection of helicopters carrying personnel and cargo from threatening air-to-air weapon-equipped helicopters
[ 本文最後由 jacklf2004 於 07-10-7 03:11 PM 編輯 ]
作者: 克里斯Chris 時間: 06-12-30 09:51
By the early 1980s, USMC aircraft inventory was declining due to attrition; a fully navalized helicopter was sought. In 1983, the USMC contracted with BHI for 44 AH-1Ws. The AH-1W Super Cobra is a day/night marginal weather Marine Corps attack helicopter that provides enroute escort for our assault helicopters and their embarked forces.
The AH-1W is a two-place, tandem-seat, twin-engine helicopter capable of land- or sea-based operations. The AH-1W provides fire support and fire support coordination to the landing force during amphibious assaults and subsequent operations ashore. The AH-1W distinguished itself with its more powerful T700-GE-401 fully marinized engines and advanced electronic weapons capability.
The AH-1W can fire TOW, Hellfire, and Sidewinder missiles and can be outfitted with Zuni rocket launchers. The AH-1W is operated in eight composite HMLA squadrons composed of 18 AH-1 and 9 UH-1 aircraft. The AH-1W is curretnly being outfitted with a Night Targeting System/Forward Looking Infrared Radar that provides laser rangefinding/designating and camera capabilities.
The AH-1W is operated in eight composite HMLA squadrons composed of 18 AH-1 and 9 UH-1 aircraft. The Marine Corps deployed 4 of 6 active force squadrons (48 AH-1Ws) to Southwest Asia during Operation Desert Shield/Desert Storm. These helicopters destroyed 97 tanks, 104 armored personnel carriers and vehicles, 16 bunkers and 2 antiaircraft artillery sites without the loss of any aircraft. The deployment required no additional augmentation to squadron support personnel and only one Bell Helicopter technical representative.
AH-1Z
A four bladed version of the AH-1W, designated the AH-1Z, is also under development; the addition of the extra blades dramatically improves the performance envelope of the AH-1W. Currently, the AH-1W is being retrofitted with a Kollsman-manufactured Night Targeting System (NTS).
The aircraft is also undergoing a cockpit reconfiguration to allow for easier copilot/gunner access to the NTS.
The upgrade of the AH-1W, including the new cockpit, is referred to as the Four Bladed AH-1W (4BW) and the upgrade of the UH-1N drive train is referred to as the Four Bladed UH-1N (4BN). Collectively, the 4BN/4BW effort constitutes the USMC H-1 Upgrades Program. The Marine Corps plans to upgrade 180 of the AH-1W gunships to the new AH-1Z standard.
The first flight is expected in October 2000, to be followed by low-rate initial production beginning in February 2002, with deliveries running from 2004 through 2013. This program combines upgrades of two USMC H-1 aircraft: the AH-1W Cobra attack helicopter and the UH-1N light utility helicopter. The common element of the two will be identical twin engines and drive trains, including a new four-bladed rotor previously developed but not fielded. In addition, the AH-1 attack helicopter will gain a new integrated cockpit and night targeting system. The upgrade will extend the life of the H-1 two models well into the 21st century.
The AH-1 will contribute to precision engagement and full-dimensional protection; the UH-1 will provide support to focused logistics.
Under the 4BW/4BN fully integrated cockpits will be phased into the development after initial work on the drive system is underway. Initial work will consist of simultaneous design efforts for the 4BW and 4BN. Major modifications include: a new rotor system with semi-automatic bladefold of the new composite rotor system, a new performance matched transmission, a new 4-bladed tail rotor and drive system, a more effective stabilizer, upgraded landing gear, tail pylon structural modifications and common cockpits. This remanufacture will add 10,000 flight hours to 4BW/4BN airframes.
The 4BW will increase aircraft maneuverability, speed, and payload (ordnance) capability. The fully integrated cockpits will reduce operator workload and improve situational awareness, thus increasing safety. It will provide growth potential for future weapon systems and avionics, which would increase mission effectiveness and survivability.
As discrete systems have previously been added to both aircraft, pilot workload has progressively worsened. The cockpits will include integration of on-board mission planning, communications, digital fire control, self navigation, night targeting, and weapons systems in nearly identical crew stations reducing training requirements. The 4BN effort will incorporate the 4BW rotor system into the UH-1N aircraft, as well as a fully integrated cockpit common with the 4BW, maximizing commonality between the two aircraft and providing needed improvements in crew and passenger survivability, payload, power available, endurance, range, airspeed, maneuverability and supportability.
The 4BN/4BW program was instituted in the summer of 1996 by combining several lesser upgrades planned but not executed by the Marine Corps. Prior to entry into EMD in September, 1996, DOT&E approved the program's alternative LFT&E plan and USD(A&T) approved a waiver from full-up, system-level LFT&E. The AH-1W will be tested full-up, system-level; the UH-1N received a waiver from full-up, system-level testing. The H-1 Upgrade ORDs require that both helicopters be tolerant to impacts by 12.7mm rounds and have crashworthy enhancements. Additionally, the drive components of the AH-1W should be tolerant to 23mm rounds.
The H-1 Upgrade has the most comprehensive and realistic aircraft LFT&E program approved to date. The program will include full-up, system-level testing of an AH-1W and testing of all but the tail (which is common to both aircraft) of the UH-1N. It will explore in detail various potential kill mechanisms related to the expected threat. The LFT&E program is integrated fully into the systems engineering effort and should yield a reasonable opportunity to incorporate improvements if deficiencies are found.
[ 本文最後由 jacklf2004 於 07-10-7 03:12 PM 編輯 ]
作者: 克里斯Chris 時間: 06-12-30 09:54
VARIANTS
Most older Cobra variants still in operation have been upgraded to the AH-1F standard. Also produced in Romania and Japan under license from Bell Textron in the U.S.
AH-1G: Initial production model in 1966AH-1S: Upgraded 1960s produced aircraft in late 1980s to the standard TOW carry-ing version.AH-1P: A set of AH-1S aircraft fitted with composite rotors, flat plate glass cockpits, and NVG capabilities.AH-1E: A set of AH-1S aircraft upgraded with the Enhanced Cobra Armament System incorporating the universal turret, 20-mm gun, automatic compensation for off-axis gun firing, and weapon management system.AH-1F: Current standard Cobra. Also referred to as the odernized Cobra Incorporated all past upgrades.| Specifications |
| Contractor: | Bell Helicopter TEXTRON, Inc. (Prime), General Electric, Kollsman Inc. |
| Power Plant: | Two General Electric T700-GE-401 Turboshaft engines Each engine delivers 1,690 horsepower. |
| Accommodations: | Two seats, in tandem (pilot in rear, copilot/gunner in front) |
| Performance: | Climb rate: 1,925 feet per minute Maximum altitude: 14,750 feet Maximum attainable speed: 170 knots (195 mph) Maximum cruising speed: 152 knots (173 mph) |
| Countermeasures: | AN/ALE-39 Chaff system and SUU-4/1 Flare dispensers |
| Armament: | One M197 three barrel 20 mm gun (mounted under the nose with 750 round ammo container) Underwing attachments for four TOW missiles, eight Hellfire missiles, or one AIM-9L Sidewinder missile Can also be equipped with Zuni rocket launchers |
External Dimensions | Main rotor diameter | 14.63 m | | Main rotor blade chord | 00.84 m | | Tail rotor diameter | 02.97 m | | Tail rotor blade chord | 00.305 m | | Distance between rotor centers | 08.89 m | | Wing span | 03.28 m | | Wing aspect ratio | 03.74 | | Length: overall, rotors turning | 17.68 m | | Length: fuselage | 13.87 m | | Width overall | 03.28 m | | Height (to top of rotor head) | 04.11 m | | Overall height | 04.44 m | | Ground clearance, main rotor, turning | 02.74 m | | Elevator span | 02.11 m | | Width over skids | 02.24 m |
| Areas | Main rotor blades (each) | 006.13 m2 | | Tail rotor blades (each) | 000.45 m2 | | Main rotor disc | 168.11 m2 | | Tail rotor disc | 006.94 m2 | | Vertical fin | 002.01 m2 | | Horizontal tail surfaces | 001.41 m2 |
|
Weights and Loadings | Weight empty | 004.634 kg | | Mission fuel load (usable) | 946 kg | | Maximum useful load (fuel and disposable ordinance) | 002.065 kg | | Maximum Takeoff and landing weight | 006.690 kg | | Maximum disc loading | 039.80 kg/m2 | | Maximum power loading | 004.42 kg/kW |
| Performance (At Maximum T-O weight, ISA) | Never exceed speed (Vne) | 190 knots | | Maximum level speed at S/L | 152 knots | | Rate of climb at S/L, OEI | 244 m/minute | | Service ceiling | More than 4,720 m | | Service ceiling, OEI | More than 3,660 m | | Hovering ceiling | | IGE | 4, 495 m | | OGE | 915 m | | Range at S/L with standard fuel, no reserves | 317 nm |
|
[ 本文最後由 jacklf2004 於 07-10-7 03:13 PM 編輯 ]
作者: 克里斯Chris 時間: 06-12-30 09:57
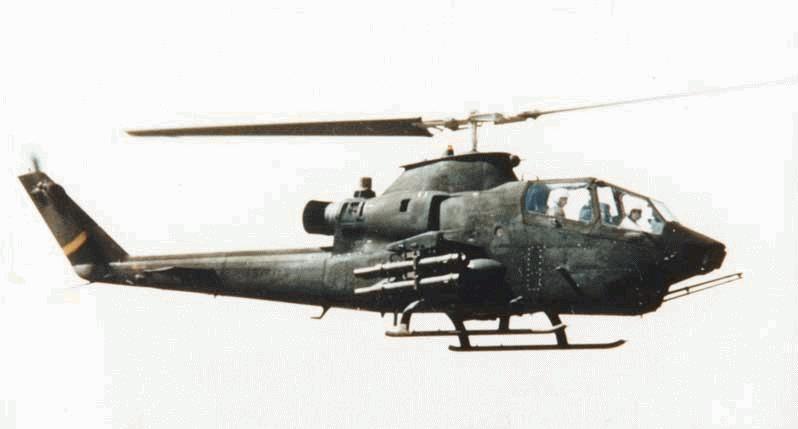
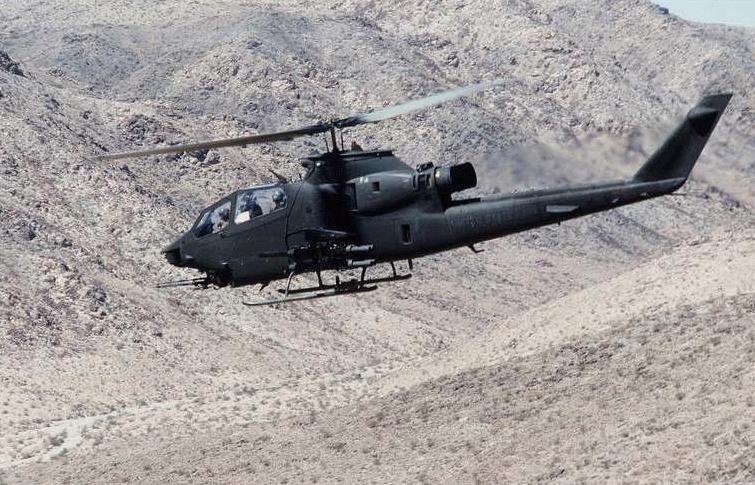
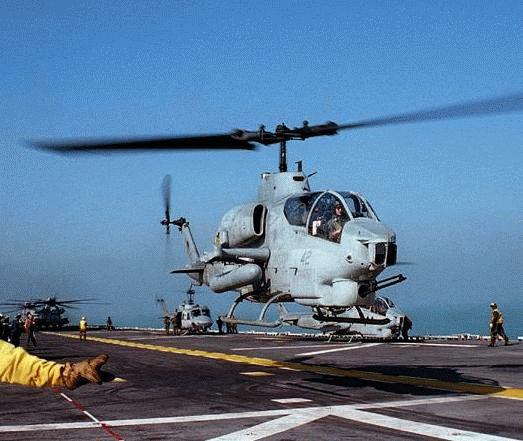
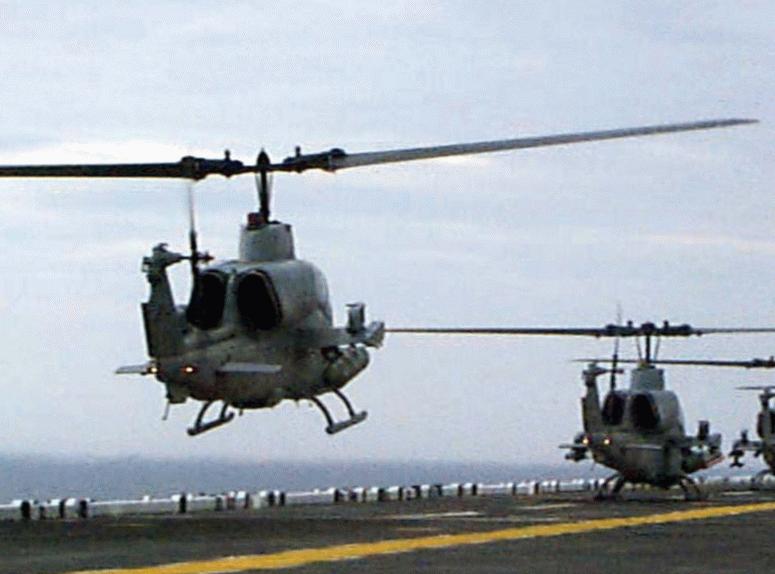
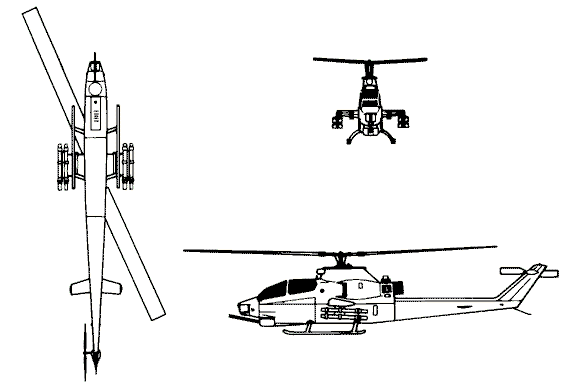





《文章來自:美陸戰隊主力攻擊直昇機》
作者: 克里斯Chris 時間: 06-12-30 09:59
武器概敘:
AH-1W超級眼鏡蛇攻擊直昇機
雖然貝爾公司與伊朗進行的廣泛交易由於巴勒維王朝的覆滅而告終止,但是貝爾對於其將伊朗AH-1J升級為AH-1T Plus的計畫深具信心,並且據此評估對美國海軍陸戰隊AH-1T進行類似改良的可能性,此計畫仍稱為AH-1T Plus。1977年貝爾向美國陸戰隊租借一架AH-1T進行改裝,換裝兩具T-700-GE-401渦輪軸發動機並試飛成功,這便是AH-1T Plus的原型機。1980年該機成功地展示在性能與經濟性的提升之後,貝爾進一步開始為其進行武器投射測試。
一開始美國陸戰隊對此一計畫並未感到很大的興趣,只讓其以最低優先層次進行,因為當時陸戰隊對換裝AH-64表現了強烈的慾望。
不過1981年國會否決陸戰隊購買AH-64的經費,加上海軍陸戰隊內部的壓力,貝爾便獲得AH-1T Plus的全面發展經費。
消息一發佈,貝爾行銷部門立刻將前述那架由AH-1T改裝而來的AH-1T Plus原型機漆上亮眼的反光黑色加上一條貫穿全機身的金色眼鏡蛇圖案。1983年此合約正式簽署時,國會批准海軍陸戰隊增購44架AH-1T Plus以減輕陸戰隊長期以來直昇機短缺的壓力。1986年3月27日當前述44架AH-1T Plus量產型的第一架出廠時,海軍陸戰隊承認AH-1T Plus所做的一切改良足以讓其賦予新的編號及命名──AH-1W超級眼鏡蛇(Super Cobra)。
除了這44架新機以及後來陸續增加的新機訂單之外,美國陸戰隊也與貝爾簽約,將原有的AH-1T逐步提升至AH-1W之水準。至於AH-1J則無法改裝至此標準,便陸續退至備役狀態。當整個計畫完成時,美國海軍陸戰隊的眼鏡蛇機隊只剩下AH-1W這一種構型。
由於換裝發動機,AH-1W的發動機艙外殼整個重新設計,全面模組化,並設有許多大型維修開口。整個發動機拆裝已經最佳化,可在數小時內完成整機拆換。此外,許多發動機外殼開口的艙蓋可疊裝成維修平台,解決直昇機在狹小空間內如運輸機機艙中不易維修之問題。發動機排氣口設有紅外線訊號抑制裝置。
早期眼鏡蛇系列將多種與拖式飛彈有關的電子儀器裝置於尾椼中以平衡機身重心,而AH-1W由於發動機的更換導致重心上移,因此這些電子儀器被移至前方機身,使得原先在此位置的20mm機砲彈藥箱必須向右挪移,因此造成機首右側多出一個突出於機身的結構物,容量750發的彈藥箱開口便設置於此。
AH-1W仍然沿襲AH-1J/T以來的弧形座艙罩,較容易產生反光而讓敵方肉眼發現,這是個小缺點。
除了換裝T-700-GE-401發動機外,AH-1W還有不少重要的改良。改良重點之一便是加裝多種航電、電戰系統,因此機身多出不少突出的結構物。
以我國採購的AH-1W為例,機上裝有ARN-118戰術空中導航儀、APN-217都卜勒戰術導航系統、APN-154(V)雷達信標器、APN-194雷達高度計、APR-39(V)2電子支援系統、APR-44(V)連續波雷達警告器、AVR-2雷達警告器、ALQ-144紅外線反制系統、加掛在短翼上方的ALE-39干擾絲投射系統、敵我識別系統、抬頭顯示器(HUD)等等。
另一重大改進便是增加AGM-114地獄火雷射導引反戰車飛彈以及AIM-9響尾蛇空對空飛彈的操作能力,爾後更增添AGM-122反輻射飛彈(衍生自AIM-9)的運用能力,能對付敵方短程防空飛彈或防空火砲的雷達系統。
值得一提的是發射AIM-9的能力,此乃美國陸軍攻擊直昇機所不具備的:由於美國海軍陸戰隊往往是第一個投入作戰的單位,並且經常要在沒有友軍支援的情況下獨自奮鬥,所以美國陸戰隊要求其所擁有的任何航空器,就算是運輸機種還是旋翼機,都必須具備一定程度的空戰能力,因為他們不一定是在美軍擁有絕對空優的情況下才作業!但美國陸軍則由於與空軍的權責劃分默契等原因,一直未能將空對空飛彈空對空飛彈納入其直昇機掛載的制式武裝之一。
此外,AH-1W依舊保留拖式飛彈的操作能力,而美國海軍陸戰隊也曾經讓AH-1W掛載AGM-65小牛空對地飛彈進行試射。在RAH-66以及AH-64D出現之前,AH-1W便是武器使用彈性最大的美製攻擊直昇機。不過一開始AH-1W並未配備雷射標定器, 在使用地獄火飛彈時需仰賴地面單位或陸戰隊軍機如A-6、OV-10、F/A-18等以雷射照射目標;直到1990年代中期以後,AH-1W才追加雷射標定系統。
受限於經費,AH-1W不得不沿用AH-1T的旋翼系統;而在AH-1系列上行之有年的平衡式兩葉片旋翼系統雖然較傳統全關節旋翼簡單、輕便且便宜,但有震動、噪音過大等問題,不僅對機身結構造成不良影響,對機上乘員的操作、舒適性等也不是件好事;此外,兩葉片旋翼系統能提供的操縱靈活度、載重能力與飛行能力也比不上四葉片旋翼系統。
事實上,貝爾當年已經發展出供超級眼鏡蛇換裝的新型複合材料製四葉片旋翼系統,在測試中不僅讓AH-1W籌載能力增加一倍多、飛行性能大幅精進,噪音和振動也減低了,但受制於經費而使換裝時程大幅延遲。
與第一流的AH-64攻擊直昇機相比,除了籌載量等攸關於機體設計的先天限制,超級眼鏡蛇唯一的不足,大概就是觀測/射控系統較為簡陋,特別是缺乏紅外線熱影像夜視系統(僅配備使用傳統夜視鏡技術的NTSF-65夜間標定系統(Night Targeting System,NTS))使其夜戰能力較AH-64大為遜色。除此之外,AH-1W的各種作戰能量與飛行性能皆與AH-64相去不遠,在武器運用彈性上則有過之而無不及。
AH-1W在1991年的波斯灣戰爭中表現出色,痛宰了伊拉克的裝甲部隊,而且後勤維修負荷以及單位時間飛行成本等皆遠低於AH-64A。
在作戰期間,50架美國陸戰隊AH-1W平均每日操作時間為13小時,派遣率高達92%,其優異的可靠度與持續戰力可見一斑。當沙漠風暴行動正式展開時,AH-1W已經全面裝設由美國陸戰隊與以色列空軍合作發展的夜間標定系統(NTS,但不具備目標定位與測距功能),以及APN-217都卜勒戰術導航系統,而前述之新型四葉旋翼系統亦在戰爭期間裝於AH-1W上進行驗證。
至1997年,美國海軍陸戰隊的AH-1W總數約達到230架,其中44架乃由AH-1T升級而來的。
AH-1W也外銷他國,土耳其擁有13架,我國則在1991年8月首次申購AH-1W,當時數量為18架,同時搭配採購12架OH-58D,代號為「陸鵬專案」;隔年採購數量增加,AH-1W增至42架而OH-58D增至26架。1992年美國批准此項採購案,1993年10月這批直昇機開始運交台灣,成為我國陸軍史上第一支專業攻擊直昇機兵力。對我國這種亞熱帶臨海小島國而言,捨美國陸軍使用的AH-1F而採購AH-1W乃是明智之舉,因為AH-1F不僅缺少AH-1W那種防止臨海氣候中鹽分、濕氣侵蝕的全機防腐蝕設計,其僅採用單發動機的設計也使其在水際環境作戰的存活率、安全性低於雙發動機的AH-1W。與美國海軍陸戰隊的AH-1W相比,我國陸軍的AH-1W少了發動機上方的兩片天線。
我國陸軍的攻擊直昇機大隊編制乃師法美國陸軍攻擊直昇機營,由兩個中隊21架AH-W以及一個中隊13架OH-58D組成;而這兩個大隊的直昇機在1997年全數運交完畢並編組成軍。爾後我國又追加訂購21架AH-1W與13架OH-58D以組建第三個攻擊直昇機大隊,其中這批增購的21架AH-1W已於2001年運交完畢。AH-1W與OH-58D的獲得不僅讓我國陸軍戰力大幅提昇,也使得我國陸軍的整體作戰觀念產生不小的變化。
AH-1W (Super Cobra)
性能諸元 |
全長: 17.68 m (主旋翼旋轉時)
主旋翼直徑: 14.63 m
尾旋翼直徑: 2.97 m
主旋翼數: 2 片
機身寬度: 3.28 m
機體長度: 13.87 m
機體全高: 4.44 m
空重: 4634 kg
最大外載: 2064 kg
最大起飛重量:6690 kg
發動機 : G.E T700-GE-401 X2
最大出力: 1723 hp(緊急時2.5分)
持續出力: 1437 hp
極速: 352 km/h
巡航速度: 278 km/h
最大爬昇率:637 m/分
實用昇限: 5486 m
最大航程: 587 km
|
[ 本文最後由 jacklf2004 於 07-10-7 03:16 PM 編輯 ]
| 歡迎光臨 鐵之狂傲 (https://gamez.com.tw/) |
|