| Specifications |
| Function | Air superiority fighter |
| Contractors | Lockheed Martin Aeronautical Systems: F-22 program management, the integrated forebody (nose section) and forward fuselage (including the cockpit and inlets), leading edges of the wings, the fins and stabilators, flaps, ailerons, landing gear and final assembly of the aircraft. Lockheed Martin Tactical Aircraft Systems: Center fuselage, stores management, integrated navigation and electronic warfare systems (INEWS), the communications, navigation, and identification (CNI) system, and the weapon support system. Boeing: wings, aft fuselage (including the structures necessary for engine and nozzle installation), radar system development and testing, avionics integration, the training system, and flight-test development and management. Pratt & Whitney: F119-PW-100 engines that power the Raptor. |
| Major Subcontractors | (partial list): Northrop Grumman, Texas Instruments, Kidde-Graviner Ltd., Allied-Signal Aerospace, Hughes Radar Systems, Harris, Fairchild Defense, GEC Avionics, Lockheed Sanders, Kaiser Electronics, Digital Equipment Corp., Rosemount Aerospace, Curtiss-Wright Flight Systems, Dowty Decoto, EDO Corp., Lear Astronics Corp., Parker-Hannifin Corp., Simmonds Precision, Sterer Engineering, TRW, XAR, Motorola, Hamilton Standard, Sanders/GE Joint Venture, Menasco Aerospace. |
| Propulsion | two Pratt & Whitney F119-PW-100 engines |
| Thrust | 35,000 lbst |
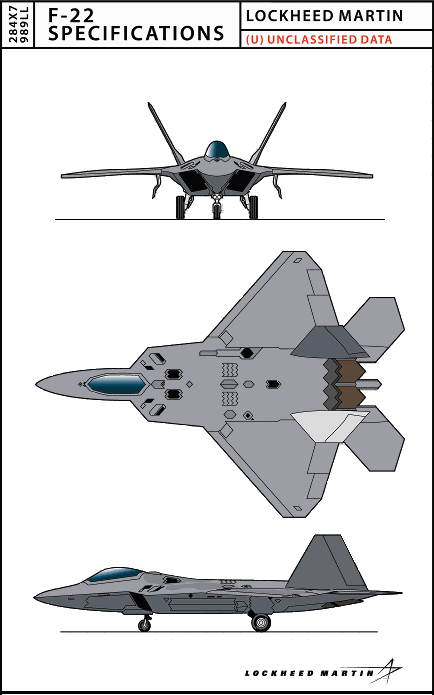
| Length | 62.08 feet, 18.90 meters |
| Height | 16.67 feet, 5.08 meters |
| Wingspan | 44.5 feet, 13.56 meters |
| Wing Area | 840 square feet |
| Horizontal Tailspan | 29 feet, 8.84 meters |
| Maximum Takeoff Weight | |
| Ceiling | |
| Speed | Mach 1.8 (supercruise: Mach 1.5) |
| Crew | one |
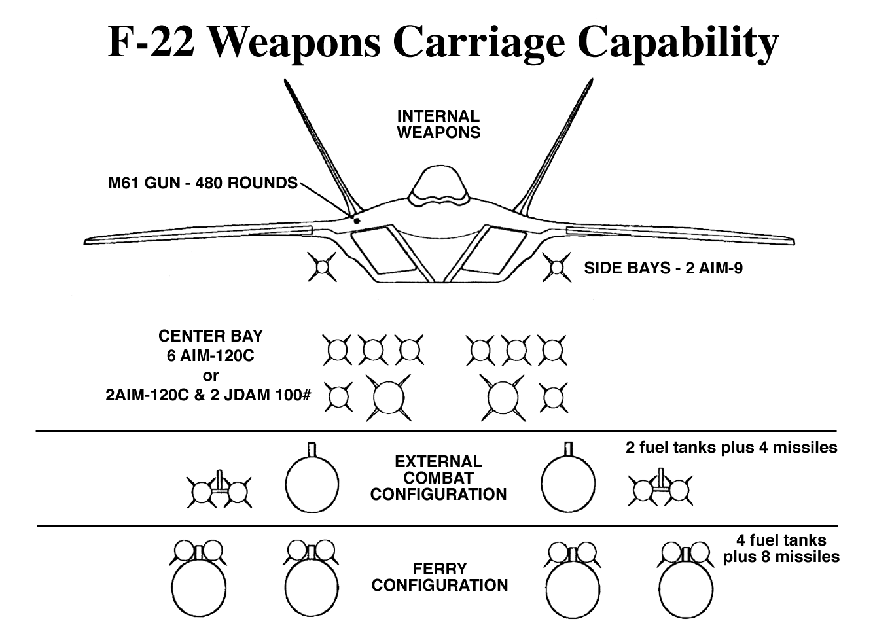
| Armament | Two AIM-9 Sidewinders six AIM-120C Advanced Medium-Range Air-to-Air Missiles (AMRAAM) one 20mm Gatling gun two 1,000-pound Joint Direct Attack Munitions (JDAM) |
| First flight: | September 7, 1997 |
| Date Deployed | deliveries beginning in 2002
operational by 2004 |