| Specifications |
| Function | strike fighter |
| Contractor | two competing teams:
Lockheed-Martin
Boeing |
| Service | U.S. Air Force | U.S. Marine Corps
U.K. Royal Navy | U.S. Navy |
| Variants | Conventional Takeoff and Landing (CTOL) | Short Takeoff and Vertical Landing (STOVL) | Carrier-based (CV) |
| Unit Cost FY94$ | $28M | $35M | $38M |
| Propulsion | Baseline: Pratt & Whitney F119-PW-100 derivative from F-22 Raptor
Alternate Engine: General Electric F120 core |
| Thrust | | | |
| Empty Weight | ~22,500 lbs | ~24,000 lbs |
| Internal Fuel | 15,000 lbs | 16,000 lbs |
| Payload | 13,000 lbs | 17,000 lbs |
| Maximum Takeoff Weight | ~50,000 lbs |
| Length | 45 feet |
| Wingspan | 36 feet | 30 feet |
| Height | | | |
| Ceiling | | | |
| Speed | supersonic |
| Combat Radius | over 600 nautical miles |
| Crew | one |
| Armament | | | |
[tr]First flight | 1999 | | Date Deployed | 2008 |
| Inventory Objectives | U.S. Air Force
2,036 aircraft | U.S. Marine Corps
642 aircraft U.K. Royal Navy
60 aircraft |
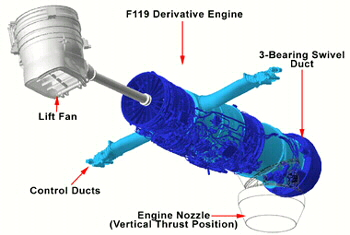
 The Lockheed Martin X-35 concept for the Marine and Royal Navy variant of the aircraft uses a shaft-driven lift-fan system to achieve Short-Takeoff/Vertical Landing (STOVL) capability. The aircraft will be configured with a Rolls-Royce/Allison shaft-driven lift-fan, roll ducts and a three-bearing swivel main engine nozzle, all coupled to a modified Pratt & Whitney F119 engine that powers all three variants.
The Lockheed Martin X-35 concept for the Marine and Royal Navy variant of the aircraft uses a shaft-driven lift-fan system to achieve Short-Takeoff/Vertical Landing (STOVL) capability. The aircraft will be configured with a Rolls-Royce/Allison shaft-driven lift-fan, roll ducts and a three-bearing swivel main engine nozzle, all coupled to a modified Pratt & Whitney F119 engine that powers all three variants. 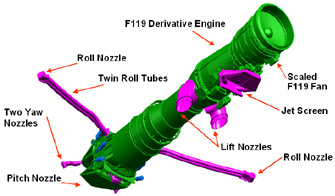
 The Boeing X-32 JSF short takeoff and vertical landing (STOVL) variant for the U.S. Marine Corps and U.K. Royal Navy employs a direct lift system for short takeoffs and vertical landings with uncompromised up-and-away performance.
The Boeing X-32 JSF short takeoff and vertical landing (STOVL) variant for the U.S. Marine Corps and U.K. Royal Navy employs a direct lift system for short takeoffs and vertical landings with uncompromised up-and-away performance. 
















