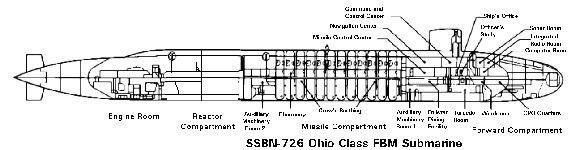
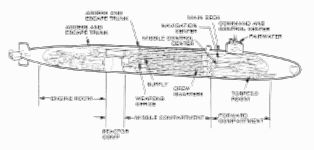
| Specifications(數據) | |
| Builders: | General Dynamics Electric Boat Division. |
| Power Plant: | One S8G nuclear reactor core reloaded every nine years two geared steam turbines, one shaft, output of 60,000 hp |
| Length: | 560 feet (170.69 meters) |
| Beam: | 42 feet (10.06 meters) |
| Displacement: | Surfaced: 16,764 tons Submerged:18,750 tons |
| Speed: | Official: 20+ knots (23+ miles per hour, 36.8 +kph) Actual: 25 knots submerged speed |
| Operating Depth: | Official: "greater than 800 feet" Actual: greater than 1,000 feet |
| Armament: | 24 - tubes for Trident I and II, 4 - torpedo tubes with Mk48 Torpedoes |
| Sensors: | BQQ-6 Bow mounted sonar BQR-19 Navigation BQS-13 Active sonar TB-16 towed array |
| Crew: | 15 Officers, 140 Enlisted |
| Unit Operating Cost Annual Average | $50,00,000 [source: [FY1996 VAMOSC] |
| Date Deployed: | November 11, 1981 (USS Ohio) |
| Boat List(同級潛艦) | GD-EB | Bangor | 1974 | 10 Apr 76 | 7 Apr 79 | 11 Nov 81 | 2023 | [tr]SSBN-727GD-EB | Bangor | 1975 | 4 Apr 77 | 26 Apr 80 | 11 Sep 82 | 2024 | [tr]SSBN-728GD-EB | Bangor | 1975 | 9 Jun 77 | 14 Nov 81 | 18 Jun 83 | 2025 | [tr]SSBN-729GD-EB | Bangor | 1976 | 7 Apr 79 | 6 Nov 82 | 11 Feb 84 | 2026 | [tr]SSBN-730GD-EB | Bangor | 1977 | 19 Jan 81 | 15 Oct 83 | 6 Oct 84 | 2026 | [tr]SSBN-731GD-EB | Bangor | 1978 | 27 Aug 81 | 19 May 84 | 25 May 85 | 2027 | [tr]SSBN-732GD-EB | Bangor | 1978 | 9 Mar 83 | 12 Jan 85 | 25 Jan 86 | 2028 | [tr]SSBN-733GD-EB | Bangor | 1980 | 8 Aug 83 | 14 Sep 85 | 16 Aug 86 | 2028 | [tr]SSBN-734GD-EB | Kings Bay | 1981 | 9 Jun 84 | 13 Dec 86 | 17 Dec 88 | 2030 | [tr]SSBN-735GD-EB | Kings Bay | 1983 | 10 Jan 84 | 23 Apr 88 | 9 Sep 89 | 2031 |




















































































| 歡迎光臨 鐵之狂傲 (https://gamez.com.tw/) |